Mold Injection: The Backbone of Scalable Product Manufacturing
Injection molding remains one of the most widely used and efficient manufacturing processes for producing high-volume plastic parts with tight tolerances and repeatable quality. From sleek consumer electronics to rugged industrial components, mold injection delivers the precision and scale needed in today’s competitive markets.
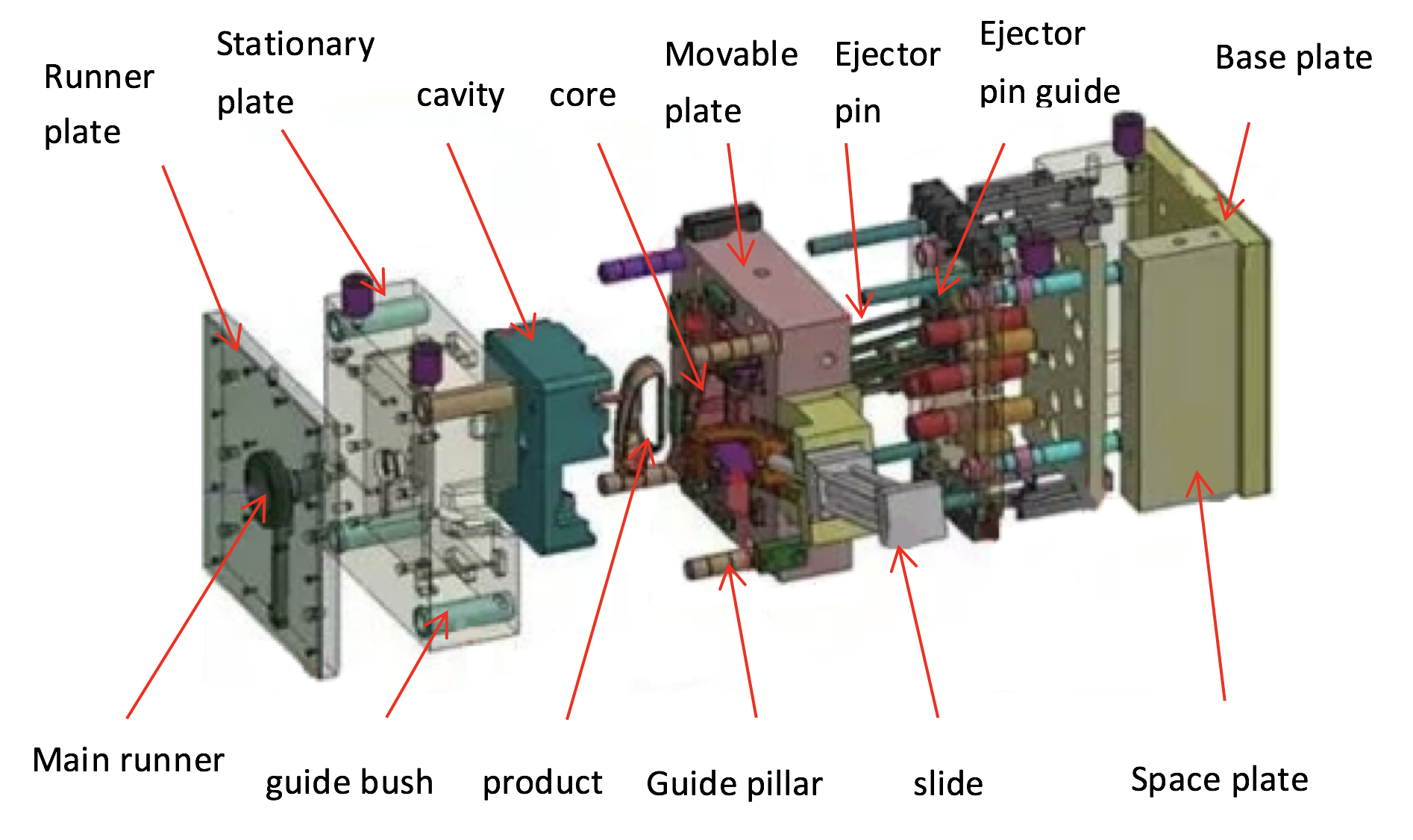
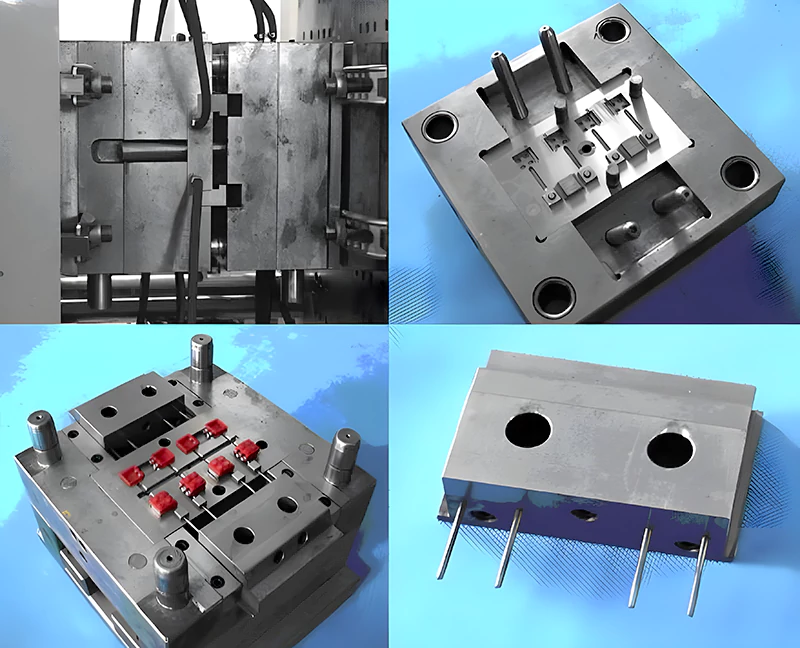
The process begins with mold design and tooling. Using CAD and simulation software, engineers optimize part geometry, gate placement, and cooling channels to prevent common issues like warping, sink marks, or short shots. Molds are typically machined from hardened steel or aluminum, depending on the production volume and material choice.
Once the tooling is complete, the injection molding machine takes over — heating plastic pellets to a molten state and injecting them into the mold cavity under high pressure. After cooling and ejection, each part is inspected for dimensional and cosmetic consistency.
Modern facilities offer a range of injection molding capabilities including:
Two-shot molding for multi-material components
Insert molding to combine plastics with metal or electronics
Overmolding for added grip, protection, or aesthetics
A wide selection of thermoplastics — such as ABS, PC, PA, and high-performance blends — allows customization for mechanical strength, chemical resistance, or UV stability.
Beyond part creation, manufacturers often provide value-added services such as ultrasonic welding, pad printing, surface texturing, and part assembly. With robust quality control and flexible production options, injection molding continues to be the go-to choice for scalable, cost-effective plastic part production.
Post time: Jun-23-2025