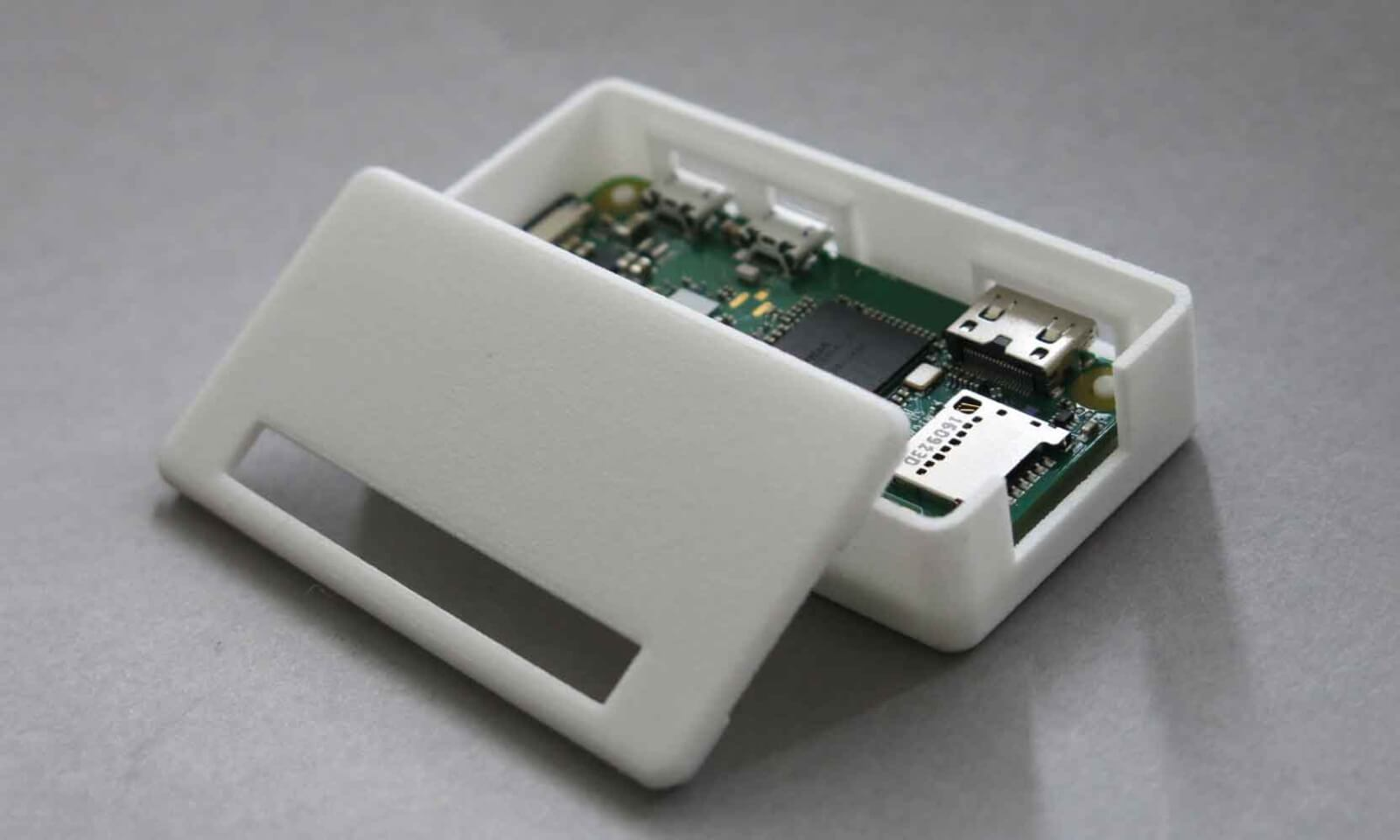
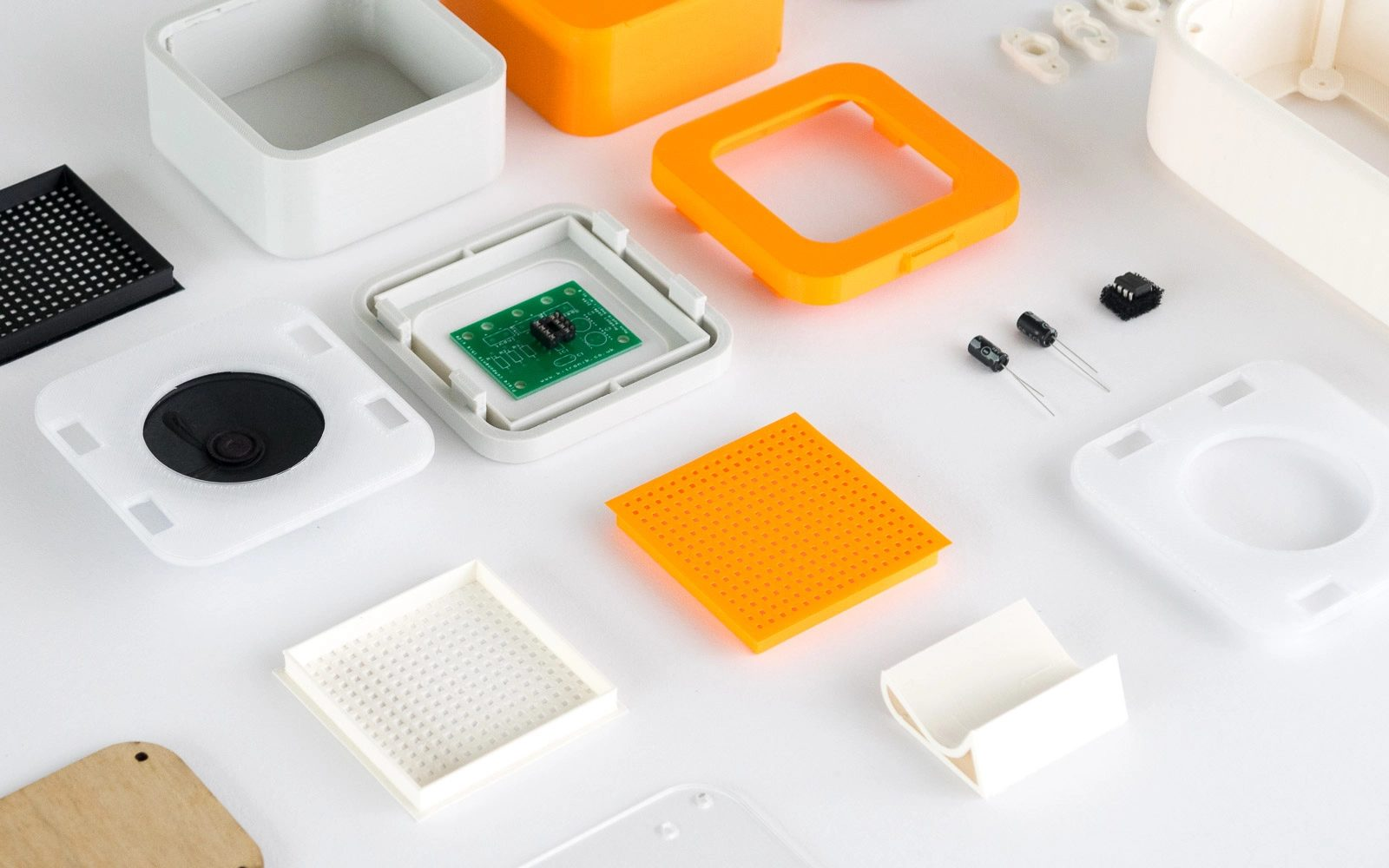
With the increasing sophistication of electronic products, the need for complex enclosure builds has never been greater. These enclosures do more than protect internal components—they enable functionality, thermal management, environmental sealing, and user interface design.
Complex enclosures often involve the integration of multiple parts and materials, including injection-molded plastics, CNC-machined aluminum, silicone gaskets, or even magnesium alloy frames. Designs may feature high IP ratings, EMI shielding, impact resistance, or heat dissipation structures—all of which require precise engineering and production control.
The enclosure development process begins with DFM (Design for Manufacturability) analysis to ensure features like snap fits, screw bosses, living hinges, and venting systems are producible and robust. Tolerance stack-up analysis is critical, especially when combining parts with varying shrink rates or material behaviors.
To meet both performance and aesthetic goals, manufacturers may apply various surface finishes such as:
Powder coating or anodizing for metals
UV coating or laser etching for plastics
Silk screen or tampo printing for branding and icons
Testing protocols for complex enclosures typically include IPX waterproof testing, drop/shock tests, thermal cycling, and fit-check validation. These ensure that the enclosure will perform reliably in real-world use conditions.
Final assembly may involve integrating touchscreens, cable routing, button interfaces, and sealing systems. The end result is a product that not only looks polished, but also stands up to physical and environmental demands—making complex enclosure builds a critical step in launching high-performance electronic devices.
Post time: Jun-19-2025