Turning Ideas into Prototypes: Required Materials and Process
Before turning an idea into a prototype, it’s crucial to gather and prepare relevant materials. This helps manufacturers accurately understand your concept and ensures the final product meets your expectations. Here is a detailed list of the necessary materials and their importance:
1. Concept Description
First, provide a detailed concept description that outlines your idea and product vision. This should include the product’s functions, uses, target user group, and market needs. A concept description helps manufacturers fully understand your idea, enabling them to develop appropriate design and manufacturing plans.
2. Design Sketches
Hand-drawn or computer-generated design sketches are essential. These sketches should be as detailed as possible, including various views of the product (front view, side view, top view, etc.) and enlarged views of key parts. Design sketches not only convey the product’s appearance but also help identify potential design issues.
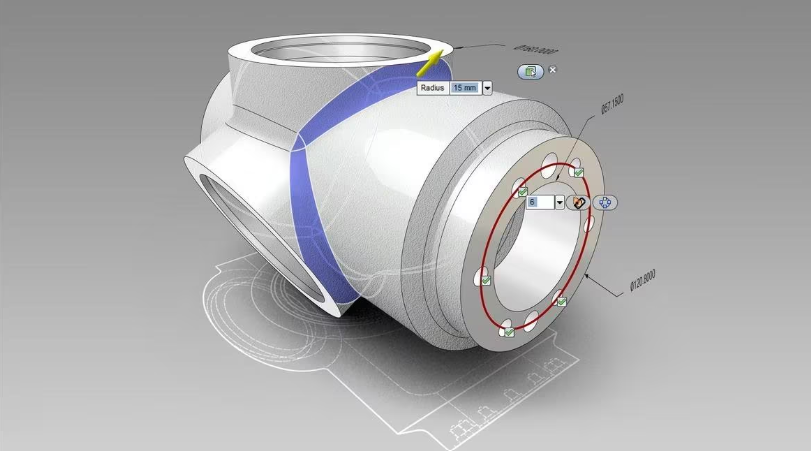
3. 3D Models
Using 3D modeling software (such as SolidWorks, AutoCAD, Fusion 360, etc.) to create 3D models provides precise structural and dimensional information about the product. 3D models allow manufacturers to perform virtual tests and adjustments before production, improving manufacturing accuracy and efficiency.
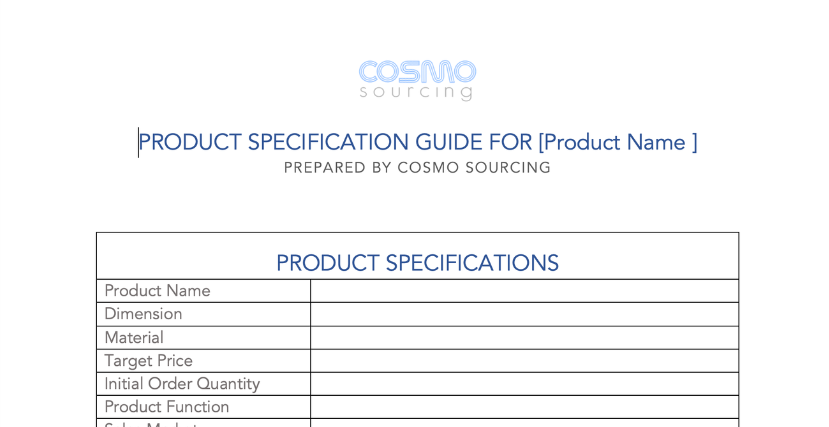
4. Technical Specifications
A detailed technical specifications sheet should include the product’s dimensions, material choices, surface treatment requirements, and other technical parameters. These specifications are crucial for manufacturers to choose the right processing techniques and materials, ensuring the product’s quality and performance.
5. Functional Principles
Provide a description of the product’s functional principles and operational methods, especially when mechanical, electronic, or software components are involved. This helps manufacturers understand the product’s operational flow and key technical requirements, ensuring it functions correctly in practical applications.
6. Reference Samples or Images
If there are reference samples or images of similar products, provide them to the manufacturer. These references can visually convey your design intentions and help manufacturers understand your specific requirements for the product’s appearance and functionality.
7. Budget and Timeline
A clear budget and timeline are essential components of project management. Providing an approximate budget range and expected delivery time helps manufacturers create a reasonable production plan and avoid unnecessary cost overruns and delays early in the project.
8. Patents and Legal Documents
If your product involves patents or other intellectual property protections, providing relevant legal documents is necessary. This not only protects your idea but also ensures that manufacturers comply with legal regulations during production.
In summary, turning an idea into a prototype requires thorough preparation of materials to ensure a smooth manufacturing process. Concept descriptions, design sketches, 3D models, technical specifications, functional principles, reference samples, budget and timeline, and related legal documents are indispensable elements. Preparing these materials not only improves manufacturing efficiency but also ensures that the final product meets expectations, helping your idea come to fruition successfully.
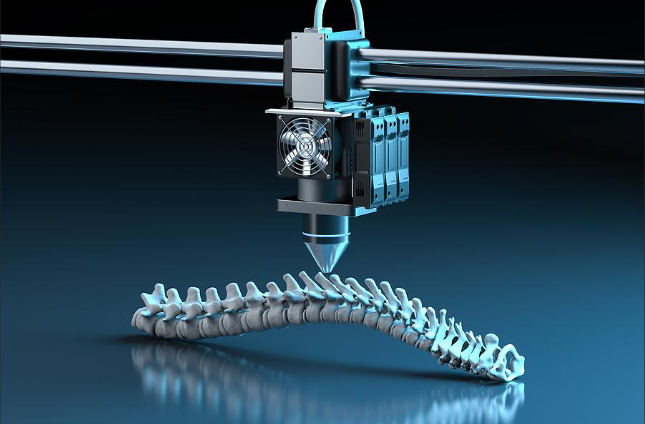
9. Selection of Prototyping Method:
Depending on the complexity, material, and purpose of the prototype, an appropriate rapid prototyping method is selected. Common methods include:
1) 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing): Building the prototype layer by layer from materials like plastics, resins, or metals.
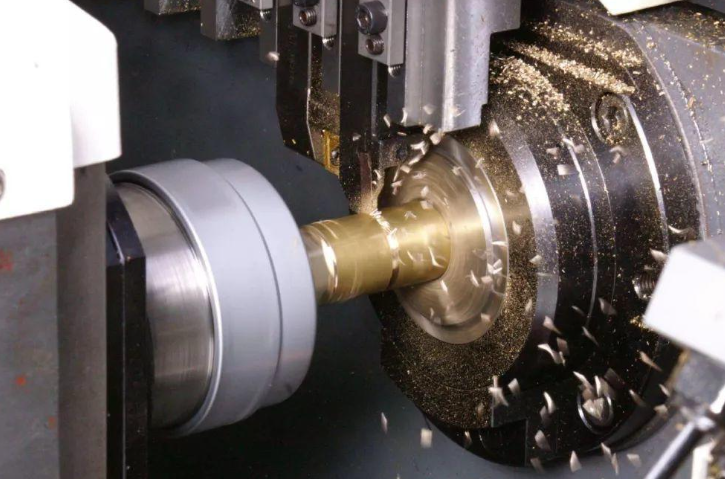
2) CNC Machining: Subtractive manufacturing, where material is removed from a solid block to create the prototype.
3) Stereolithography (SLA): A 3D printing technique that uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic.
4) Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Another 3D printing method that fuses powder material using a laser to create solid structures.
10. Testing and evaluation
The prototype is then tested for various factors such as fit, form, function, and performance. Designers and engineers assess whether it meets the desired specifications and identify any flaws or areas for improvement.
Based on feedback from testing, the design may be modified and a new prototype created. This cycle can be repeated multiple times to refine the product.
Once the prototype meets all design and functional requirements, it can be used to guide the production process or as a proof-of-concept for stakeholders.
Rapid prototyping is essential in modern design and manufacturing for creating innovative products efficiently and effectively.
Post time: Aug-12-2024